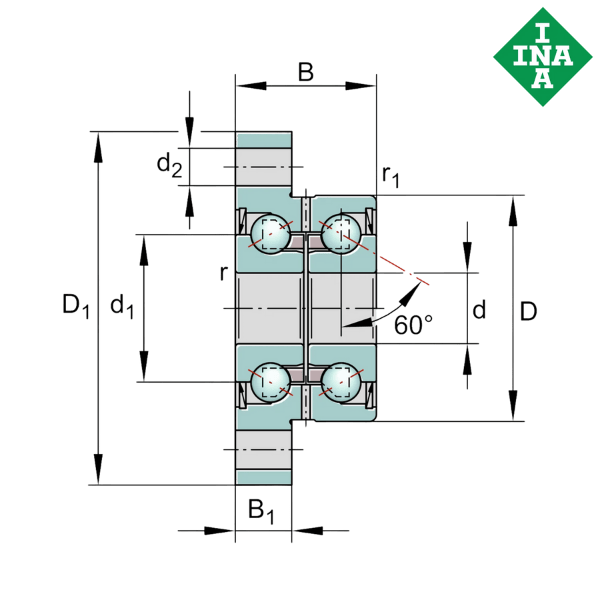
Understanding Standardized Boundary Dimensions in Bearings

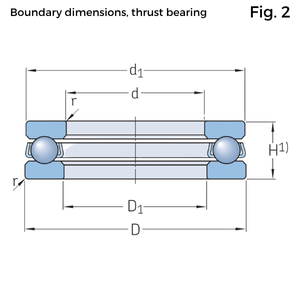
• Bore diameter (d)
• Outside diameter (D)
• Width or height (B, C, T, or H)
• Chamfer dimensions (r)
These dimensions are globally standardized under ISO guidelines to maintain consistency across manufacturers. For instance:
• ISO 15 governs radial rolling bearings
• ISO 104 covers thrust bearings
• ISO 355 applies to tapered roller bearings
The ISO general plan for radial bearings defines a range of standardized outside diameters corresponding to each standard bore diameter. These are categorized as diameter series, numbered 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4—progressing in order of increasing outside diameter. Within each diameter series, there are various width series, labeled 8, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, arranged by increasing width. Combinations of diameter series 0, 2, and 3 with width series 0 to 3 are illustrated in Fig 13.
In the case of thrust bearings, height series are used in place of width series. These height series are numbered 7, 9, 1, and 2.

Bearings that conform to the ISO general plans have identical boundary dimensions when they share the same bore diameter and dimension series (as detailed in table 3). Otherwise, their dimensions will vary.
Additionally, SKF offers a broad selection of inch-dimensioned bearings, which comply with American and British standards, complementing their ISO-compliant product range.

Prefixes and suffixes

• Prefixes are primarily used to identify individual components of a bearing or to indicate a specific variant of the bearing.
• Suffixes describe design modifications or variations from the original or current basic design.
Suffixes are organized into specific groups, and when multiple features need to be specified, the suffixes appear in a defined sequence as outlined in Fig 4. For detailed meanings of specific prefixes and suffixes, refer to the relevant product sections in the catalogue.
Other rolling bearings
Rolling bearings not covered in the ball bearings and roller bearings sections, such as super-precision bearings, thin section bearings, slewing bearings or linear bearings, follow designation systems that can differ significantly from the basic designation system.
Conclusion
Understanding standardized boundary dimensions is essential for selecting the right bearing and ensuring compatibility across machinery and suppliers. ISO-defined series for bore diameter, outside diameter, width, and height help manufacturers and engineers maintain global consistency and simplify replacement. Whether working with metric or inch-dimensioned bearings, adhering to these standards guarantees accurate fitment, reliable performance, and easier sourcing. For more details please visit this page.